A power transformer is a machine that transfers power from circuit to circuit with constant frequency. It is a static device because of the unavailability of moving or rotating parts. Their operation depends on the principle of mutual induction over an AC supply.
World-class power transformers are manufactured in Vadodara, in the state of Gujarat by GUJARAT TRANSFORMERS. The brand is well known because of its performance in the market for 55 years. These industrial steam turbines can cater to 45 MW capacities up to 150 MW. Here is all that you need to know about power transformers:
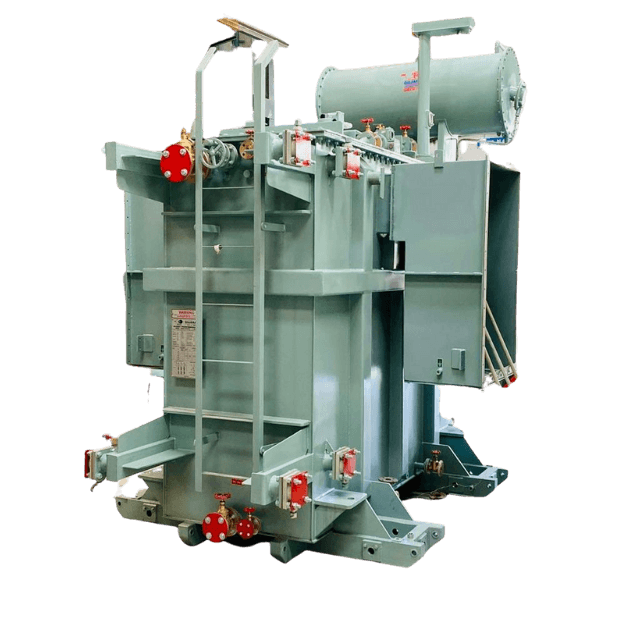
Parts
These are the parts of a power transformer:
- Conservator – above the main tank, conserves the transformer oil.
- Steel Tank – the most crucial part, houses the windings, core, and other essential parts.
- Core – provides a path with low reluctance for the flow of magnetic flux.
- Buchholz Relay – protective device senses issues within the transformer.
- Breather – consists of silica gel, traps moisture from the air entering the transformer
- Windings – turns of copper coils, classified based on input, output, and voltage.
- Cooling Tubes – cool down the transformer oil.
- Tap Changer – balances the voltage in the transformer.
- Thermometer – used above 50KVA values, measures temperature within the transformer.
- Explosion Vent – above the conservator, expels boiling hot water out of the transformer.
Advantages
There are many benefits to the use of a power transformer, some of which are stated below:
- Easy construction and working principle
- Ability to step up and down the voltage and current
- Provide galvanic isolation with high efficiency, simple production, and reliability.
- Smooth power generation, transmission, and quick distribution.
- Cost-efficient.
- Types of transformers vary according to power, current, distribution, potential, and isolation.
- No internal moving parts and a long starting time.
- The potential to be reverse connected is dependent on usage type.
- Various input voltages are accommodated with multiple taps.
Disadvantages
Where power transformers are very advantageous, there are some cons attached to their usage:
- Require constant cooling and maintenance.
- It cannot perform the same functions under DC supply.
- Iron and load losses occur when the transformer is energized or under-load.
- Technology criteria don’t match the current requirements.
- Mostly, they are cumbersome and bulky.
- Offer limited power and voltage quality regulation.
- Often undergoes frequency variations and voltage dips.
- Imbalanced harmonics.
Design
Designing the magnetic components of a transformer is challenging because of the high demands of modern electronics. These twelve basic steps are essential to ensure a successful project:
- Adequate adjustment of input voltage ranges
- Maintenance of output voltage range.
- Calculation of the output power or current.
- Measuring switch frequency.
- Selecting the operating mode.
- Assuring a maximum duty cycle of the IC.
- Meeting the safety requirements.
- Adjusting the ambiance of temperature.
- Comprehending the size requirements.
Conclusion
Modern devices cannot function under old parameters with the modern age of technicality and digital requirements. Newer laptops, internet devices, smartphones, and connection systems require specific essential components to meet the usage criteria. If electricity is not managed in accordance with the flow of power, the results are dissatisfactory. Power transformers are, therefore, very important to ensure a constant flow of electricity under the most fluctuant conditions.


